When it comes to your home’s foundation, the stakes couldn’t be higher. The foundation’s health directly impacts the structural integrity of your entire home. And among the various types of foundations, pier and beam stand out as a time-tested method, particularly popular in areas with expansive soils or where flooding might be a concern. The intricacies of pier and beam foundation spacing (and everything else in between), however, often raise many worrisome questions. Let’s try to answer them, as understanding these aspects can be the difference between a solid foundation and one that gradually fails over time.
First, What Are Foundation Piers?
Foundation piers are deep, supportive structures that transfer the load of a building down to a stable soil layer or bedrock. Unlike slab foundations, which spread the load over a large area, pier foundations concentrate the load on specific points, allowing for construction on uneven terrain or soil with low bearing capacity.

These piers are typically constructed from materials such as concrete, steel, or wood. Depending on the soil conditions and the specific requirements of the building, they can be driven, drilled, or poured. The piers work in conjunction with beams, which distribute the load across them. Together, they form a grid that effectively supports the structure above.
Pier And Beam Foundation Spacing Explained
In a pier and beam foundation, piers are spaced out strategically across the footprint of the building, supporting horizontal beams that, in turn, support the floor joists and the structure’s weight. This design creates a crawl space beneath the house, offering several advantages over slab-on-grade foundations.

The crawl space, typically between 18 inches to 4 feet high, allows easy access to plumbing, electrical wiring, and HVAC systems. It also acts as a buffer against ground moisture. However, this type of foundation requires careful attention to detail, especially regarding the spacing of the piers.
The Importance Of Proper Pier And Beam Foundation Spacing
The spacing of foundation piers is not just a matter of structural integrity; it’s about ensuring the long-term health and stability of the building. Incorrectly spaced piers mean uneven load distribution, which can cause floors to sag, walls to crack, or doors and windows to stick. Over time, these issues can exacerbate, leading to costly repairs or, in severe cases, catastrophic failure of the foundation.
Factors Influencing Pier Spacing
Several factors influence the spacing of piers, including the weight of the building, the type of soil, the size of the beams, and local building codes. Typically, piers are spaced between 5 to 8 feet apart, but this can vary depending on the project’s specifics.
Building Load
One of the primary determinants of pier spacing is the load the foundation must support. This includes the weight of the structure itself, as well as additional loads such as furniture, appliances, occupants, and environmental factors like snow or wind.
Simply put, heavier buildings require more piers or piers closer together to distribute the load effectively.
Soil Conditions
Soil type plays a crucial role in calculating how close or far apart the piers should be. Piers can often be spaced further apart in areas with stable, compacted soil or bedrock close to the surface. Conversely, in regions with expansive clay, loose sand, or other unstable soils, piers set closer together will prevent shifting or settling.
Beam Size And Material
Larger, more substantial beams can span greater distances between piers without sagging, allowing for wider spacing. However, smaller or weaker beams require piers placed closer together to prevent structural issues.
Local Building Codes
Building codes vary by region. They take into account local environmental conditions, such as soil type and weather patterns, and provide guidelines for minimum and maximum pier spacing. Make sure to consult these codes during the design phase of a pier and beam foundation to avoid potential legal and structural issues.
Common Pier Spacing Guidelines
While the specific pier and beam foundation spacing can vary depending on the factors mentioned above, some general guidelines are commonly followed in residential construction:
- For typical residential structures: Piers are generally spaced 5 to 8 feet apart.
- For larger buildings or those with heavy loads: Spacing may be reduced to 3 to 5 feet.
- In areas with poor soil conditions: Closer spacing is required, sometimes as close as 3 feet apart.
- For lighter structures or in areas with firm, stable soil: Spacing can be increased to 8 to 10 feet or more.
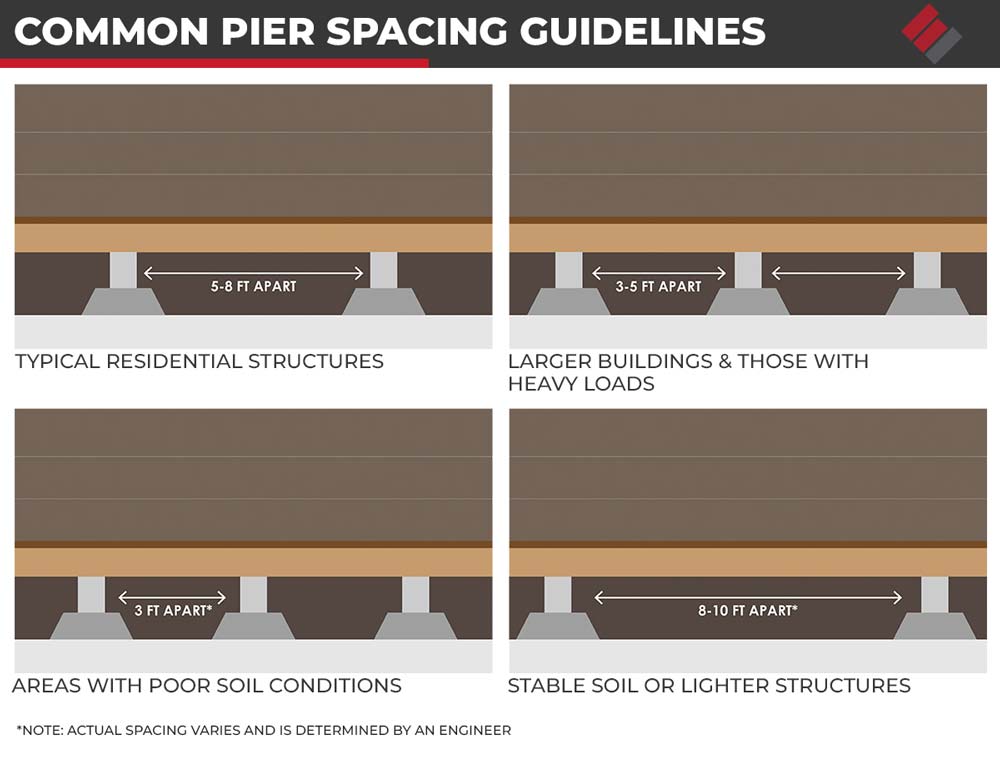
It’s important to note that these are just general guidelines, and the actual spacing should be determined by a structural engineer assessing the specific conditions of your site.
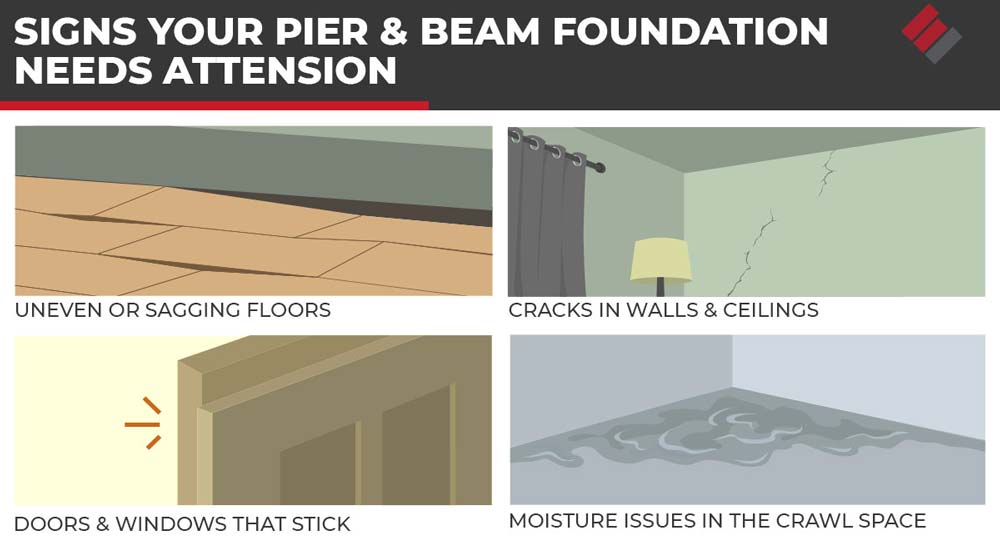
Signs That Your Pier And Beam Foundation Needs Attention
Even with proper pier spacing, a pier and beam foundation may require maintenance over time. Here are some signs that you might need to have your foundation inspected or repaired:
- Uneven or Sagging Floors: This often indicates that one or more piers have settled or shifted, causing the beams to become uneven.
- Cracks in Walls and Ceilings: They may start small and gradually widen if the underlying issue is not addressed.
- Doors and Windows That Stick: If your doors or windows begin to stick or fail to close correctly, it could be a sign that your foundation is shifting. This is often caused by the piers settling unevenly, leading to frame misalignment.
- Moisture Issues in the Crawl Space: If you notice excessive moisture, mold, or mildew, it could be a sign that the foundation is not performing as it should. This moisture can weaken the beams and piers over time, leading to more significant issues.
Repairing And Maintaining Your Pier And Beam Foundation
Maintaining a pier and beam foundation involves regular inspections and timely repairs. The following steps can help ensure the longevity and stability of your foundation:
Replacing Or Adding Piers
In some cases, piers may need to be replaced due to damage or added to improve the foundation’s stability. This can be a complex process, especially if the piers are difficult to access or if the soil conditions are challenging. However, it’s a necessary step to ensure the foundation’s long-term stability.
- One typical case is when the existing piers have deteriorated due to rot, termite damage, or prolonged exposure to moisture, which compromises their ability to support the structure.
- Another situation arises when the soil beneath the piers shifts or erodes, causing uneven settling that can lead to structural imbalances.
- Adding extra levels to a house typically requires supplemental piers to accommodate the increased load.
- In some cases, adding new piers can solve the problems of poor original construction or inadequate pier spacing, and restore stability.
Each of these scenarios requires careful assessment by a professional to determine the best course of action.
Addressing Moisture Issues
Moisture is one of the biggest threats to a pier and beam foundation. To prevent damage, ensure that the crawl space is adequately ventilated and that any water drainage systems around your home function correctly.
If you notice moisture buildup, consider installing a vapor barrier or improving the drainage around your home.
Re-Leveling The Foundation
It’s not uncommon for a pier and beam foundation to require re-leveling over time. This process involves raising the foundation and adding or adjusting the piers to ensure the structure is level and stable.
Re-leveling should be performed by professionals to ensure that it’s done correctly and safely.
Regular Inspections
Routine inspections will let you discover potential issues before they become major problems. Ideally, you should inspect your foundation at least once a year, paying close attention to the crawl space and the condition of the piers and beams.
Look for signs of moisture, rot, or insect damage, as well as any shifting or settling of the piers.
Ensure Your Piers Are Correctly Spaced!
Addressing any issues as (or before) they arise is the right path to prevent costly repairs and maintain your home’s structural integrity.
If you’re concerned about the condition of your pier and beam foundation or if you’ve noticed signs of damage, don’t wait to take action. Request a quote today for professional crawl space repair services and protect your home from foundation issues before they escalate!







